Design Process
Design Thinking Framework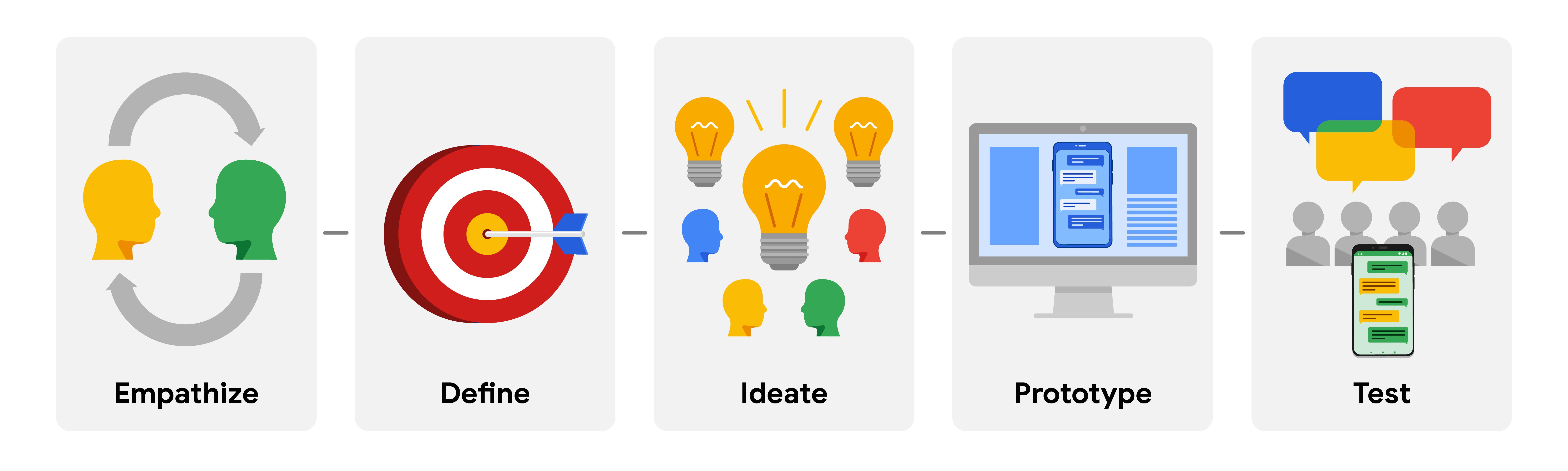
I take on a Design Thinking Approach
The design thinking framework is based on the philosophy that a hands-on, user-centric approach to problem solving promotes innovation; in turn, innovation can lead to differentiation and a competitive advantage. The design-thinking process is composed of 5 distinct phases.
1. Empathize:
Goal: Understand the user’s perspective, needs, and challenges deeply.
- User Research: Conduct interviews, surveys, and observations to gather qualitative and quantitative data.
- User Personas: Create detailed profiles representing different user segments.
- Empathy Maps: Visualize user thoughts, feelings, and actions to empathize with their experiences.
- Journey Mapping: Document the user’s interactions with a product or service to identify pain points and opportunities.
2. Define:
Goal: Clearly articulate the problem based on user insights.
- Problem Statement: Summarize the core problem from the user’s perspective.
- Point of View (POV): Reframe the problem as a focused and actionable statement.
- HMW (How Might We) Questions: Pose questions that inspire creative solutions.
- Constraints and Considerations: Define limitations, such as budget, time, and resources.
3. Ideate:
Goal: Generate a wide range of creative ideas to solve the defined problem.
- Brainstorming: Encourage free-flowing idea generation within a team.
- Mind Mapping: Visualize relationships between ideas and concepts.
- Concept Sketching: Create rough visual representations of potential solutions.
- Worst Possible Idea: Explore the extreme end of possibilities to challenge assumptions.
4. Prototype:
Goal: Build a tangible representation of the solution concepts.
- Low-Fidelity Prototypes: Create basic and rough representations using paper, cardboard, or digital tools.
- Medium-Fidelity Prototypes: Develop more detailed and interactive prototypes using software or 3D modeling.
- High-Fidelity Prototypes: Build polished and realistic prototypes with advanced functionalities.
- Iterative Prototyping: Continuously refine and improve the prototypes based on feedback.
5. Test:
Goal: Gather user feedback on the prototypes to inform further iterations.
- User Testing: Observe users interacting with the prototypes and gather feedback.
- Feedback Analysis: Analyze user responses to identify patterns and insights.
- Iteration: Modify and refine the prototypes based on user feedback.
- A/B Testing: Compare different versions of the prototype to determine the most effective solution.
Related Videos
Photography
Weekday Evenings
7PM -10PM
Weekends
1 PM - 11 PM
Contact
Phone
+(562) 552 2526
info@michaelserna.design
Address
Riverside, California
